
Kathmandu, March 10: Nepal Rastra Bank (NRB), the central bank of Nepal, has informed that remittance inflows have increased 21.6 percent to Rs.839 billion in the past seven months.
According to a report “Current Macroeconomic and Financial Situation of Nepal” (Based on Seven Months Data Ending Mid-February, 2023/24), in the US Dollar terms, remittance inflows increased 19.1 percent to 6.31 billion in the review period compared to an increase of 16.4 percent in the same period of the previous year.
In the review period, the number of Nepali workers, both institutional and individual, taking first-time approval for foreign employment stands at 247,012 and taking approval for renew entry stands at 158,540. In the previous year, such numbers were 314,767 and 167,708 respectively.
Net transfer increased 20.0 percent to Rs.910.74 billion in the review period. Such a transfer had increased 25.2 percent in the same period of the previous year.
Current Account and Balance of Payments
The current account remained at a surplus of Rs.161.69 billion in the review period against a deficit of Rs.40.16 billion in the same period of the previous year. In the US Dollar terms, the current
account registered a surplus of 1.22 billion in the review period against a deficit of 314.6 million in the same period last year.
In the review period, capital transfer decreased 29.0 percent to Rs.3.80 billion and net foreign direct investment (FDI) remained a positive of Rs.5.18 billion. In the same period of the previous year, capital transfer amounted to Rs.5.35 billion and net FDI amounted to Rs.1.04 billion.
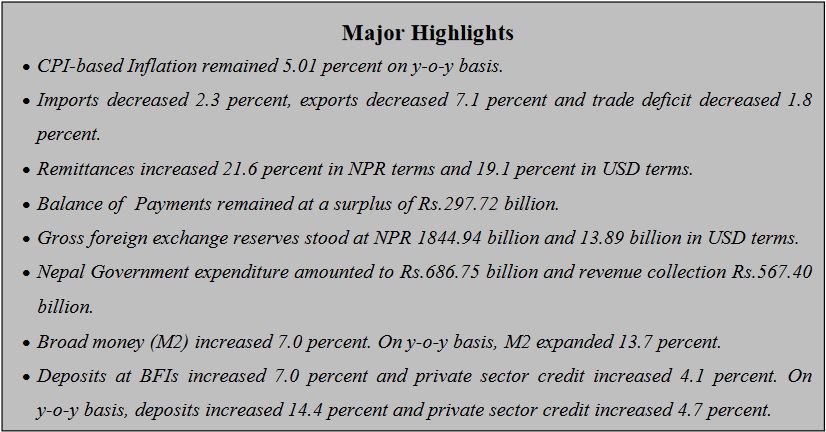
Balance of Payments (BOP) remained at a surplus of Rs.297.72 billion in the review period against a surplus of Rs.128.55 billion in the same period of the previous year. In the US Dollar terms, the
BOP remained at a surplus of 2.24 billion in the review period against a surplus of 975.7 million in the same period of the previous year.
Foreign Exchange Reserves
Gross foreign exchange reserves increased 19.9 percent to Rs.1844.94 billion in mid-February 2024 from Rs.1539.36 billion in mid-July 2023. In the US dollar terms, the gross foreign exchange
reserves increased 18.6 percent to 13.89 billion in mid-February 2024 from 11.71 billion in mid-July 2023.
Of the total foreign exchange reserves, reserves held by NRB increased 20.7 percent to Rs.1623.92 billion in mid-February 2024 from Rs.1345.78 billion in mid- July 2023. Reserves held by banks and financial institutions (except NRB) increased 14.2 percent to Rs.221.02 billion in mid-February 2024 from Rs.193.59 billion in mid-July 2023. The share of Indian currency in total reserves stood at 22.6 percent in mid- February 2024.
Foreign Exchange Adequacy Indicators
Based on the imports of seven months of 2023/24, the foreign exchange reserves of the banking sector is sufficient to cover the prospective merchandise imports of 14.7 months, and merchandise
and services imports of 12.3 months.
The ratio of reserves-to-GDP, reserves-to-imports and reserves-to-M2 stood at 34.3 percent, 102.4 percent and 28.0 percent respectively in mid-February 2024. Such ratios were 28.6 percent, 83.0 percent and 25.0 percent respectively in mid-July 2023.
Merchandise Trade
During the review period, merchandise exports decreased 7.1 percent to Rs.86.83 billion compared to a decrease of 29 percent in the same period of the previous year. Destination-wise, exports to India and other countries decreased 11.3 percent and 2 percent whereas exports to China increased 338.8 percent.
Exports of zinc sheet, particle board, juice, readymade garments, ginger among others increased whereas exports of palm oil, soyabean oil, cardamom, tea, woolen carpet, among others decreased.
FULL TEXT
Current-Macroeconomic-and-Financial-Situation-English-Based-on-Seven-Months-data-of-2023.24











