
Kathmandu, March 11: The latest financial indicators as of Magh end, 2081 BS (Mid-February 2025) reveal that Class “A” commercial banks continue to dominate Nepal’s banking sector in terms of deposits, loans, and financial outreach. The report highlights a stark contrast in key financial ratios among Class “A”, Class “B”, and Class “C” financial institutions.
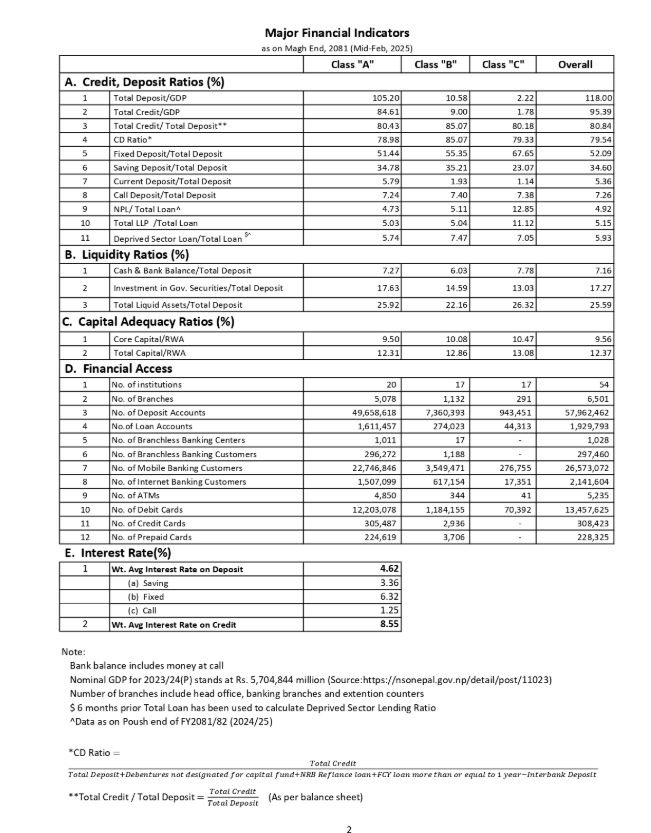
Class “A” banks recorded a CD ratio of 78.98%, significantly higher than Class “B” (85.07%) and Class “C” (79.33%). Likewise, total deposits in Class “A” banks amounted to 105.20% of GDP, vastly overshadowing Class “B” (10.58%) and Class “C” (2.22%). Similarly, total credit issuance was 84.61% of GDP for Class “A”, compared to 9.0% for Class “B” and 1.78% for Class “C”.
Liquidity indicators show that Class “A” banks held 7.27% of their total deposits in cash and bank balance, while Class “B” and Class “C” institutions maintained 6.03% and 7.78%, respectively. Investments in government securities as a percentage of total deposits were also the highest for Class “A” banks at 17.63%, followed by Class “C” (14.59%) and Class “B” (13.03%).
In terms of capital adequacy, Class “C” institutions maintained the highest Core Capital to Risk-Weighted Assets (RWA) ratio at 13.08%, while Class “A” banks stood at 12.31% and Class “B” at 12.86%.
With a total with 5,078 branches, Class “A” banks remained 20, Class B as 17 and Class C banks remained as 17. They also account for the largest number of deposit accounts (57.92 million) and loan customers (1.93 million).
According to NRB, the number of mobile banking customers have reached at 26.57 million, number of internet banking customers stood at 2.14 million, number of debit cards as 13.46 million and number of ATMs stood as 5,235.
The banks have maintained a lower rate for credit facilities. According to NRB, the banks have been offering credit on a rate of 8.55% on average. #nepal #finance
Full Report
finance report










